Laser cutting is a popular and versatile method used to precisely cut and shape metal parts. Whether you’re working on prototypes, custom designs, or large production runs, laser cutting offers exceptional accuracy and speed. However, to ensure you get the best results and avoid costly mistakes, there are a few important considerations to keep in mind before sending your metal parts to a fabrication shop. In this blog post, we’ll explore five key things you should know before laser cutting your parts.
1. Material Selection is Crucial
The type of metal you choose plays a significant role in the laser cutting process. Different metals have varying properties that can affect the quality, speed, and cost of cutting.
- Common Materials for Laser Cutting: Laser cutting works well with a wide range of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. However, each material requires different cutting settings, such as laser power, cutting speed, and gas type.
- Material Thickness: The thickness of the metal also affects the cutting process. Thicker materials require higher laser power and slower cutting speeds, which can increase costs and lead times. On the other hand, thinner materials are quicker and less expensive to cut, but may have a different cut quality.
- Material Coatings: If your metal has a coating (e.g., galvanized or painted), it may need to be removed or considered during the cutting process. Coatings can interfere with the laser’s ability to cut cleanly and may even damage the equipment.
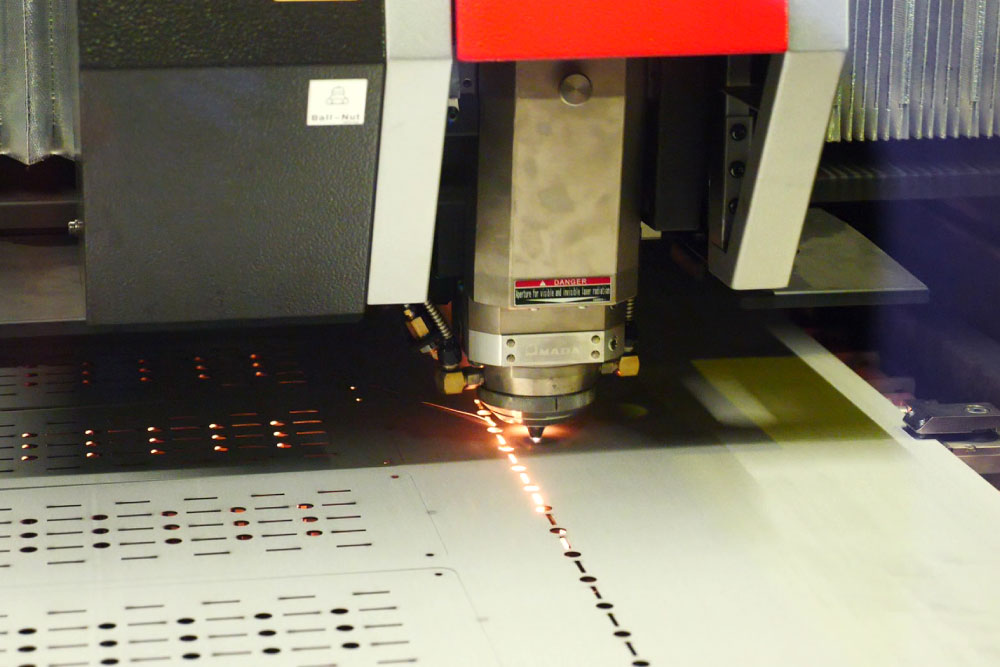

2. Understand the Laser Cutting Technology
Laser cutting machines come in various types, each suited to different applications. The two most common types are CO2 lasers and fiber lasers, each with its own set of advantages and considerations.
- CO2 Lasers: CO2 lasers are versatile and effective for cutting non-metals as well as metals. They tend to be less efficient for cutting thick metals compared to fiber lasers but are commonly used for cutting thinner sheets of material, especially stainless steel and aluminum.
- Fiber Lasers: Fiber lasers are more efficient when cutting thicker metals and are known for faster cutting speeds, higher precision, and lower energy consumption compared to CO2 lasers. They’re ideal for metals like mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, particularly for thinner to mid-range thicknesses.
- Cut Quality: Different laser types can result in different cut edge qualities. Fiber lasers, for instance, typically provide a cleaner cut with less burr formation than CO2 lasers, especially in metals like aluminum. It’s important to ask your fabrication shop about the specific technology they use and how it aligns with your material and project requirements.
3. Tolerances and Precision Requirements
Laser cutting is renowned for its precision, but it’s important to understand the tolerances required for your parts. If your project demands high levels of accuracy, make sure the fabrication shop can meet those expectations.
- Standard Tolerances: Typically, laser cutting provides a tolerance range of +/- 0.005 inches, but this can vary depending on the material thickness and complexity of the design. Thinner materials generally offer better tolerances.
- Complex Geometries: Intricate designs with small details or tight tolerances may require more careful planning. Ensure the shop is capable of handling the level of detail your parts require. Providing digital files with clear specifications will help minimize errors.
- Edge Finish: Laser cutting can produce smooth, clean edges, but if a specific finish or surface treatment is required (e.g., deburring or polishing), discuss this with the fabrication shop in advance. Additional post-processing steps may be necessary to achieve the desired result.

4. Consider the Cutting Speed and Efficiency
Laser cutting is fast, but cutting speed varies depending on several factors such as material type, thickness, and the complexity of the design.
- Cutting Speed: Thicker materials require slower cutting speeds due to the increased time it takes to penetrate the material. For example, cutting 1/8-inch steel is much quicker than cutting a 1-inch plate. The complexity of the design, such as tight curves or intricate patterns, can also slow down the cutting process.
- Efficiency vs. Quality: While it’s tempting to focus on cutting speed for quick turnaround, compromising on quality for speed could lead to undesirable outcomes. If the part has critical dimensions or surface finishes, it’s better to prioritize accuracy over speed to avoid mistakes.
- Cost Considerations: Faster cuts may lead to lower costs, but this can vary depending on material and design. It’s important to balance cost, time, and quality to find the best approach for your project.
5. File Preparation and Design Considerations
The quality of the final laser-cut parts depends heavily on the design files provided. Accurate, well-prepared files are essential for smooth processing and optimal results.
- File Formats: Laser cutting machines typically work with vector-based file formats like DXF, DWG, or SVG. Be sure to provide a clean, editable file that clearly represents your design.
- Design Guidelines: When preparing your design, there are certain considerations to keep in mind. For example, ensure that the lines are set to the appropriate thickness for cutting, avoid overly sharp internal corners (which can be difficult to cut), and maintain proper spacing between elements to prevent issues with the laser beam.
- Kerf and Material Loss: The laser beam has a width, known as the “kerf,” which causes a slight loss of material at the cut edges. Make sure to account for the kerf in your design, especially for parts that need to fit together precisely.
Conclusion
Laser cutting is an invaluable tool for creating high-quality metal parts with precision and speed. However, understanding the factors that affect the laser cutting process can help you avoid delays, reduce costs, and ensure the final parts meet your specifications. By considering material selection, laser technology, tolerances, cutting speed, and file preparation, you can optimize the process and get the best possible results for your project.
Before you send your parts to a fabrication shop, make sure to communicate these considerations clearly. A good fabrication partner will work with you to ensure your designs are executed flawlessly and efficiently. So, next time you’re preparing to laser cut metal parts, keep these five points in mind to achieve the best outcome.
